

|
|
|||||||
في حال وجود أي مواضيع أو ردود
مُخالفة من قبل الأعضاء، يُرجى الإبلاغ عنها فورًا باستخدام أيقونة
![]() ( تقرير عن مشاركة سيئة )، و الموجودة أسفل كل مشاركة .
( تقرير عن مشاركة سيئة )، و الموجودة أسفل كل مشاركة .
| آخر المواضيع |
|
|
|
أدوات الموضوع | انواع عرض الموضوع |
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 1 | ||||
|
ارجو منكم المساعدة في بحث الانجليزية حول الكوارث الطبيعية اذا كان عندكم هذا البحث من قبل الرجاء تحطوهلي او تعطوني فيديوات واغاني حول الكوارث الطبيغية
|
||||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 2 | |||
|
اخي انا عندي حول التصحر عروض باور بونت وصور ورح احاول ارفعهم و شكرا |
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 3 | ||||
|
اقتباس:
يمكنك أن تختار ما تحتاج من هذا البحث Natural disaster From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search A natural disaster is the effect of a natural hazard (e.g., flood, tornado, hurricane, volcanic eruption, earthquake, or landslide). It leads to financial, environmental or human losses. The resulting loss depends on the vulnerability of the affected population to resist the hazard, also called their resilience.[1] This understanding is concentrated in the formulation: "disasters occur when hazards meet vulnerability."[2] A natural hazard will hence never result in a natural disaster in areas without vulnerability, e.g. strong earthquakes in uninhabited areas. The term natural has consequently been disputed because the events simply are not hazards or disasters without human involvement.[3] A concrete example of the division between a natural hazard and a natural disaster is that the 1906 San Francisco earthquake was a disaster, whereas earthquakes are a hazard. This article gives an introduction to notable natural disasters, refer to the list of natural disasters for a comprehensive listing. Geological disasters Avalanches Main article: List of avalanches See also: Avalanche   Avalanche on the backside (East) of Mt. Timpanogos, Utah at Aspen Grove trail Notable avalanches include:
Main article: List of earthquakes See also: Earthquake An earthquake is a sudden shake of the Earth's crust caused by the tectonic plates colliding.The vibrations may vary in magnitude. The underground point of origin of the earthquake is called the "focus". The point directly above the focus on the surface is called the"epicenter". Earthquakes by themselves rarely kill people or wildlife. It is usually the secondary events that they trigger, such as building collapse, fires, tsunamis (seismic sea waves) and volcanoes, that are actually the human disaster. Many of these could possibly be avoided by better construction, safety systems, early warning and evacuation planning.Earthquakes are caused by the discharge of energy accumulated along geologic fault. Some of the most significant earthquakes in recent times include:
Main article: List of largest volcanic eruptions See also: Types of volcanic eruptions Volcanoes can cause widespread destruction and consequent disaster through several ways. The effects include the volcanic eruption itself that may cause harm following the explosion of the volcano or the fall of rock. Second, lava may be produced during the eruption of a volcano. As it leaves the volcano the lava destroys any buildings and plants it encounters. Third, volcanic ash generally meaning the cooled ash - may form a cloud, and settle thickly in nearby ********s. When mixed with water this forms a concrete-like material. In sufficient quantity ash may cause roofs to collapse under its weight but even small quantities will harm humans if inhaled. Since the ash has the consistency of ground glass it causes abrasion damage to moving parts such as engines. The main killer of humans in the immediate surrounding of an volcanic eruption is the pyroclastic flows, which consist of a cloud of hot volcanic ash which builds up in the air above the volcano and rushes down the slopes when the eruption no longer supports the lifting of the gases. It is believed that Pompeii was destroyed by a pyroclastic flow. A lahar is a volcanic mudflow or landslide. The 1953 Tangiwai disaster was caused by a lahar, as was the 1985 Armero tragedy in which the town of Armero was buried and an estimated 23,000 people were killed. A specific type of volcano is the supervolcano. According to the Toba catastrophe theory 70 to 75 thousand years ago a super volcanic event at Lake Toba reduced the human population to 10,000 or even 1,000 breeding pairs creating a bottleneck in human evolution. It also killed three quarters of all plant life in the northern hemisphere. The main danger from a supervolcano is the immense cloud of ash which has a disastrous global effect on climate and temperature for many years. Hydrological disasters Main article: List of floods See also: Flooding   The Limpopo River, in southern Mozambique, during the 2000 Mozambique flood Some of the most notable floods include:
See also: Limnic eruption   A cow suffocated by gases from Lake Nyos after a limnic eruption A limnic eruption occurs when a gas, usually CO2 suddenly erupts from deep lake water, posing the threat of suffocating wildlife, livestock and humans. Such an eruption may also cause tsunamis in the lake as the rising gas displaces water. Scientists believe landslides, volcanic activity, or explosions can trigger such an eruption. To date, only two limnic eruptions have been observed and recorded:
Main article: Historic tsunamis See also: Tsunami   The tsunami caused by the December 26, 2004, earthquake strikes Ao Nang, Thailand. Tsunamis can be caused by undersea earthquakes as the one caused in Ao Nang, Thailand, by the 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake, or by landslides such as the one which occurred at Lituya Bay, Alaska.
See also: Meteorological disasters   Young steer after a blizzard, March 1966 Blizzards See also: Blizzard Blizzards are severe storms characterized by low temperature, strong winds, and heavy snow. The difference between a Blizzard and a snow storm is the strength of the wind. To be a considered a blizzard, the storm must have winds in excess of 35 miles per hour, it should reduce the visibility to 1/4th miles, and must last for a prolonged period of 3 hours or more. Ground Blizzards require high winds to stir up snow that has already fallen, rather than fresh snowfall. Blizzards have a negative impact on local economics and can terminate the visibility in regions where snowfall is rare. The 1972 IRAN Blizzard resulted in approximately 4,000 deaths and lasted for 5 to 7 days. Significant blizzards in the United States include:
Main article: List of tropical cyclones See also: Tropical cyclone and Cyclone Cyclone, tropical cyclone, hurricane, and typhoon are different names for the same phenomenon a cyclonic storm system that forms over the oceans. The deadliest hurricane ever was the 1970 Bhola cyclone; the deadliest Atlantic hurricane was the Great Hurricane of 1780 which devastated Martinique, St. Eustatius and Barbados. Another notable hurricane is Hurricane Katrina which devastated the Gulf Coast of the United States in 2005. Droughts See also: Drought Well-known historical droughts include:
See also: Hail Hailstorms are rain drops that have formed together into ice. A particularly damaging hailstorm hit Munich, Germany, on July 12, 1984, causing about 2 billion dollars in insurance claims. Heat waves See also: Heat wave The worst heat wave in recent history was the European Heat Wave of 2003.   Hurricane Katrina A summer heat wave in Victoria, Australia, caused the massive bushfires in 2009. Melbourne experienced three days in a row of temperatures exceeding 40°C. The bushfire, otherwise known as "Black Saturday" was also started intentionally. Tornadoes Main article: List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks See also: Tornado  This section requires expansion. This section requires expansion.A tornado (often referred to as a twister or, erroneously, a cyclone) is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, but are typically in the form of a visible condensation funnel, whose narrow end touches the earth and is often encircled by a cloud of debris and dust. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than 110 miles per hour (177 km/h), are approximately 250 feet (80 m) across, and travel a few miles (several kilometers) before dissipating. The most extreme can attain wind speeds of more than 300 mph (480 km/h), stretch more than two miles (3 km) across, and stay on the ground for dozens of miles (more than 100 km).[1][2][3] Fires Main article: List of forest fires See also: Wildfire Wildfires are an uncontrolled fire burning in wildland areas. Common causes include lightning and drought but wildfires may also be started by human negligence or arson. They can be a threat to those in rural areas and also wildlife. Notable cases of wildfires were the 1871 Peshtigo Fire in the United States, which killed at least 1700 people, and the 2009 Victorian bushfires in Australia. Health disasters Epidemics Main article: List of epidemics See also: Epidemics 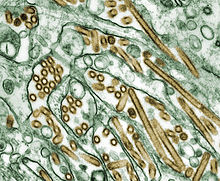  The A H5N1 virus, which causes Avian influenza An epidemic is an outbreak of a contractible disease that spreads at a rapid rate through a human population. A pandemic is an epidemic whose spread is global. There have been many epidemics throughout history, such as Black Death. In the last hundred years, significant pandemics include:
Main article: List of famines See also: Famine In modern times, famine has hit Sub-Saharan Africa the hardest, although the number of victims of modern famines is much smaller than the number of people killed by the Asian famines of the 20th century. Space disasters   Fallen trees caused by the Tunguska meteoroid of the Tunguska event in June 1908. Impact events See also: impact event  This section requires expansion. This section requires expansion.One of the largest impact events in modern times was the Tunguska event in June 1908. Solar flares See also: solar flare A solar flare is a phenomenon where the sun suddenly releases a great amount of solar radiation, much more than normal. Some known solar flares include:
External links
|
||||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 4 | |||
|
بارك الله فيك عمو |
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 5 | |||
|
The forest may have little impact on flooding in the case of large rainfall events, which overwhelm the storage capacity of forest soil if the soils are at or close to saturation. Tropical rainforests produce about 30% of our planet's fresh water Soil Deforestation for the use of clay in the Brazilian city of Rio de Janeiro. The hill depicted is Morro da Covanca, in Jacarepaguá Undisturbed forests have a very low rate of soil loss, approximately 2 metric tons per square kilometer (6 short tons per square mile).[citation needed] Deforestation generally increases rates of soil erosion, by increasing the amount of runoff and reducing the protection of the soil from tree litter. This can be an advantage in excessively leached tropical rain forest soils. Forestry operations themselves also increase erosion through the development of roads and the use of mechanized equipment. China's Loess Plateau was cleared of forest millennia ago. Since then it has been eroding, creating dramatic incised valleys, and providing the sediment that gives the Yellow River its yellow color and that causes the flooding of the river in the lower reaches (hence the river's nickname 'China's sorrow'). Removal of trees does not always increase erosion rates. In certain regions of southwest US, shrubs and trees have been encroaching on grassland. The trees themselves enhance the loss of grass between tree canopies. The bare intercanopy areas become highly erodible. The US Forest Service, in Bandelier National Monument for example, is studying how to restore the former ecosystem, and reduce erosion, by removing the trees. Tree roots bind soil together, and if the soil is sufficiently shallow they act to keep the soil in place by also binding with underlying bedrock. Tree removal on steep slopes with shallow soil thus increases the risk of landslides, which can threaten people living nearby. However most deforestation only affects the trunks of trees, allowing for the roots to stay rooted, negating the landslide. Ecological Deforestation results in declines in biodiversity.[45] The removal or destruction of areas of forest cover has resulted in a degraded environment with reduced biodiversity.[46] Forests support biodiversity, providing habitat for wildlife;[47] moreover, forests foster medicinal conservation.[48] With forest biotopes being irreplaceable source of new drugs (such as taxol), deforestation can destroy genetic variations (such as crop resistance) irretrievably.[49] Since the tropical rainforests are the most diverse ecosystems on Earth[50][51] and about 80% of the world's known biodiversity could be found in tropical rainforests,[52][53] removal or destruction of significant areas of forest cover has resulted in a degraded[54] environment with reduced biodiversity.[55] It has been estimated that we are losing 137 plant, animal and insect species every single day due to rainforest deforestation, which equates to 50,000 species a year.[56] Others state that tropical rainforest deforestation is contributing to the ongoing Holocene mass extinction.[57][58] The known extinction rates from deforestation rates are very low, approximately 1 species per year from mammals and birds which extrapolates to approximately 23,000 species per year for all species. Predictions have been made that more than 40% of the animal and plant species in Southeast Asia could be wiped out in the 21st century.[59] Such predictions were called into question by 1995 data that show that within regions of Southeast Asia much of the original forest has been converted to monospecific plantations, but that potentially endangered species are few and tree flora remains widespread and stable.[60] Scientific understanding of the process of extinction is insufficient to accurately make predictions about the impact of deforestation on biodiversity.[61] Most predictions of forestry related biodiversity loss are based on species-area models, with an underlying assumption that as the forest declines species diversity will decline similarly.[62] However, many such models have been proven to be wrong and loss of habitat does not necessarily lead to large scale loss of species.[62] Species-area models are known to overpredict the number of species known to be threatened in areas where actual deforestation is ongoing, and greatly overpredict the number of threatened species that are widespread.[60] Reducing emissions Main article: Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation Major international organizations, including the United Nations and the World Bank, have begun to develop programs aimed at curbing deforestation. The blanket term Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) describes these sorts of programs, which use direct monetary or other incentives to encourage developing countries to limit and/or roll back deforestation. Funding has been an issue, but at the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties-15 (COP-15) in Copenhagen in December 2009, an accord was reached with a collective commitment by developed countries for new and additional resources, including forestry and investments through international institutions, that will approach USD 30 billion for the period 2010 - 2012.[114] Significant work is underway on tools for use in monitoring developing country adherence to their agreed REDD targets. These tools, which rely on remote forest monitoring using satellite imagery and other data sources, include the Center for Global Development's FORMA (Forest Monitoring for Action) initiative [115] and the Group on Earth Observations' Forest Carbon Tracking Portal.[116] Methodological guidance for forest monitoring was also emphasized at COP-15 [117] The environmental organization Avoided Deforestation Partners leads the campaign for development of REDD through funding from the U.S. government.[118] Solutions to Deforestation The safe keeping of our precious planet lies with each and every member of its human population. We are the ones accountable for our actions even though it is ourselves we are accountable too. We have the power and knowledge to turn this planet into a green and pleasant place to live or to completely destroy all life. Deforestation is one of the major pressing environmental issues we face and one we must address the solutions to and quickly if we are to restore the damage we have done to the environment. |
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 6 | |||
|
The forest may have little impact on flooding in the case of large rainfall events, which overwhelm the storage capacity of forest soil if the soils are at or close to saturation. Tropical rainforests produce about 30% of our planet's fresh water Soil Deforestation for the use of clay in the Brazilian city of Rio de Janeiro. The hill depicted is Morro da Covanca, in Jacarepaguá Undisturbed forests have a very low rate of soil loss, approximately 2 metric tons per square kilometer (6 short tons per square mile).[citation needed] Deforestation generally increases rates of soil erosion, by increasing the amount of runoff and reducing the protection of the soil from tree litter. This can be an advantage in excessively leached tropical rain forest soils. Forestry operations themselves also increase erosion through the development of roads and the use of mechanized equipment. China's Loess Plateau was cleared of forest millennia ago. Since then it has been eroding, creating dramatic incised valleys, and providing the sediment that gives the Yellow River its yellow color and that causes the flooding of the river in the lower reaches (hence the river's nickname 'China's sorrow'). Removal of trees does not always increase erosion rates. In certain regions of southwest US, shrubs and trees have been encroaching on grassland. The trees themselves enhance the loss of grass between tree canopies. The bare intercanopy areas become highly erodible. The US Forest Service, in Bandelier National Monument for example, is studying how to restore the former ecosystem, and reduce erosion, by removing the trees. Tree roots bind soil together, and if the soil is sufficiently shallow they act to keep the soil in place by also binding with underlying bedrock. Tree removal on steep slopes with shallow soil thus increases the risk of landslides, which can threaten people living nearby. However most deforestation only affects the trunks of trees, allowing for the roots to stay rooted, negating the landslide. Ecological Deforestation results in declines in biodiversity.[45] The removal or destruction of areas of forest cover has resulted in a degraded environment with reduced biodiversity.[46] Forests support biodiversity, providing habitat for wildlife;[47] moreover, forests foster medicinal conservation.[48] With forest biotopes being irreplaceable source of new drugs (such as taxol), deforestation can destroy genetic variations (such as crop resistance) irretrievably.[49] Since the tropical rainforests are the most diverse ecosystems on Earth[50][51] and about 80% of the world's known biodiversity could be found in tropical rainforests,[52][53] removal or destruction of significant areas of forest cover has resulted in a degraded[54] environment with reduced biodiversity.[55] It has been estimated that we are losing 137 plant, animal and insect species every single day due to rainforest deforestation, which equates to 50,000 species a year.[56] Others state that tropical rainforest deforestation is contributing to the ongoing Holocene mass extinction.[57][58] The known extinction rates from deforestation rates are very low, approximately 1 species per year from mammals and birds which extrapolates to approximately 23,000 species per year for all species. Predictions have been made that more than 40% of the animal and plant species in Southeast Asia could be wiped out in the 21st century.[59] Such predictions were called into question by 1995 data that show that within regions of Southeast Asia much of the original forest has been converted to monospecific plantations, but that potentially endangered species are few and tree flora remains widespread and stable.[60] Scientific understanding of the process of extinction is insufficient to accurately make predictions about the impact of deforestation on biodiversity.[61] Most predictions of forestry related biodiversity loss are based on species-area models, with an underlying assumption that as the forest declines species diversity will decline similarly.[62] However, many such models have been proven to be wrong and loss of habitat does not necessarily lead to large scale loss of species.[62] Species-area models are known to overpredict the number of species known to be threatened in areas where actual deforestation is ongoing, and greatly overpredict the number of threatened species that are widespread.[60] Reducing emissions Main article: Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation Major international organizations, including the United Nations and the World Bank, have begun to develop programs aimed at curbing deforestation. The blanket term Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) describes these sorts of programs, which use direct monetary or other incentives to encourage developing countries to limit and/or roll back deforestation. Funding has been an issue, but at the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties-15 (COP-15) in Copenhagen in December 2009, an accord was reached with a collective commitment by developed countries for new and additional resources, including forestry and investments through international institutions, that will approach USD 30 billion for the period 2010 - 2012.[114] Significant work is underway on tools for use in monitoring developing country adherence to their agreed REDD targets. These tools, which rely on remote forest monitoring using satellite imagery and other data sources, include the Center for Global Development's FORMA (Forest Monitoring for Action) initiative [115] and the Group on Earth Observations' Forest Carbon Tracking Portal.[116] Methodological guidance for forest monitoring was also emphasized at COP-15 [117] The environmental organization Avoided Deforestation Partners leads the campaign for development of REDD through funding from the U.S. government.[118] Solutions to Deforestation The safe keeping of our precious planet lies with each and every member of its human population. We are the ones accountable for our actions even though it is ourselves we are accountable too. We have the power and knowledge to turn this planet into a green and pleasant place to live or to completely destroy all life. Deforestation is one of the major pressing environmental issues we face and one we must address the solutions to and quickly if we are to restore the damage we have done to the environment. |
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 7 | |||
|
thank you so much but if you have any video for any disaster i wish that you can give it to me |
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 8 | |||
|
|
|||
|
|
رقم المشاركة : 9 | |||
|
بخصوص الفديوهات تفضل هذا و دور فيه ( الحرب العالمية الأولى مليانة كوارث طبيعية بسبب الانسان ) |
|||
|
|
المشاركات المنشورة تعبر عن وجهة نظر صاحبها فقط، ولا تُعبّر بأي شكل من الأشكال عن وجهة نظر إدارة المنتدى
المنتدى غير مسؤول عن أي إتفاق تجاري بين الأعضاء... فعلى الجميع تحمّل المسؤولية
Powered by vBulletin .Copyright آ© 2018 vBulletin Solutions, Inc